Recognizing Hyperglycemia: Understanding the Signs and Safeguarding Your Health
Hyperglycemia, or high blood glucose levels, is a condition that often arises in individuals with diabetes but can also affect those who are pre-diabetic or even without a diabetes diagnosis in some cases. It typically occurs when the body fails to produce enough insulin or isn’t able to use insulin effectively. Recognizing the symptoms of hyperglycemia is essential for preventing serious health complications. In this blog post, we will discuss the signs to look out for, the potential causes, and the importance of effective management.
Signs and Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
The symptoms of hyperglycemia can vary in intensity. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms that are easily overlooked, while others may have more severe reactions. Here are common signs that indicate high blood sugar levels:
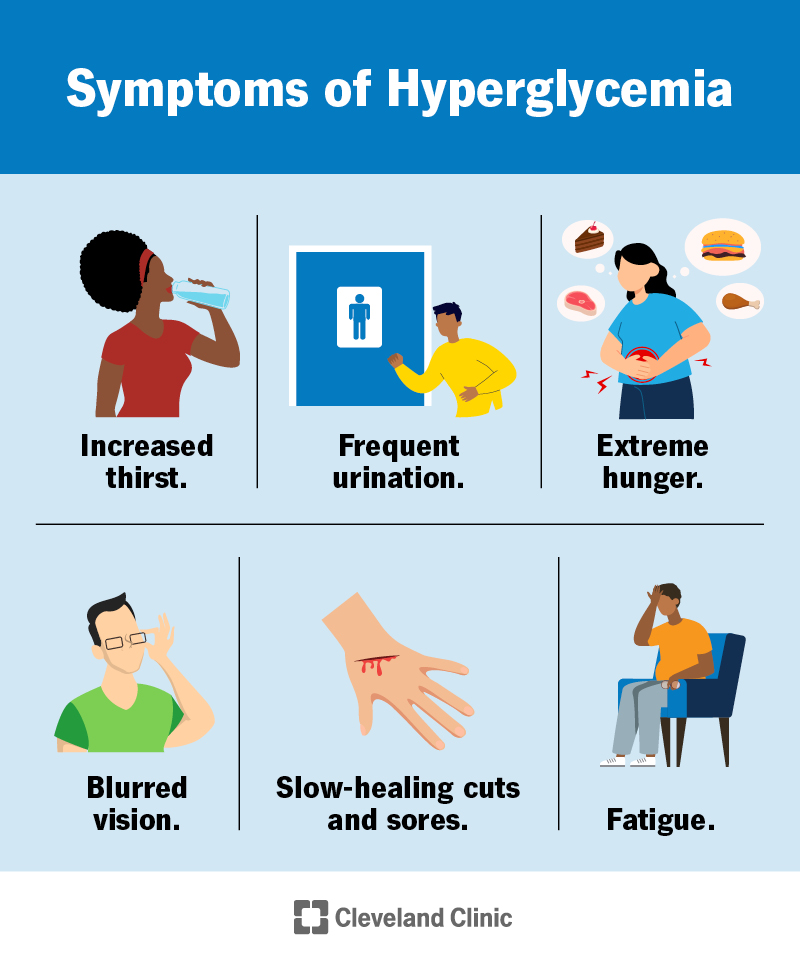
- Increased Thirst (Polydipsia): One of the earliest signs of hyperglycemia is excessive thirst. When blood sugar levels rise, the body attempts to dilute the excess glucose in the blood, leading to dehydration and an insatiable need for fluids.
- Frequent Urination (Polyuria): Elevated glucose levels cause the kidneys to filter out the surplus sugar. This process can result in an increase in urine production, leading to frequent bathroom visits.
- Fatigue: High blood sugar can impact energy levels. Individuals may feel unusually tired and lethargic as the body struggles to regulate glucose levels and cells become starved of energy.
- Blurred Vision: Fluctuations in blood glucose levels can lead to changes in the lenses of the eyes, causing temporary blurriness. Persistent high blood sugar can eventually lead to more serious eye problems.
- Headaches: Some individuals report frequent headaches when experiencing hyperglycemia, which could arise from dehydration or changes in blood chemistry.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Cognitive function can be impaired when blood sugar levels remain elevated, leading to feelings of confusion or diminished focus.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: In more severe cases, the body may begin to break down muscle and fat for energy, leading to significant weight loss.
Causes of Hyperglycemia
Understanding what triggers hyperglycemia can help individuals take preventive measures. Common causes include:
- Dietary Choices: Consuming a diet high in carbohydrates and sugars can lead to spikes in blood glucose levels.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise can contribute to insulin resistance, making it harder for the body to manage glucose.
- Illness or Stress: Infections, fever, or emotional stress can increase hormone levels that raise blood sugar.
- Medications: Certain medications, particularly corticosteroids, can elevate blood sugar levels.
- Insufficient Insulin: For those who have diabetes, not taking enough insulin or other medications can lead to hyperglycemia.
The Importance of Management
Recognizing and managing hyperglycemia is crucial not only for individuals with diabetes but also for those at risk. If left untreated, prolonged high blood sugar can lead to serious complications, including:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a life-threatening condition more common in type 1 diabetes.
- Long-term complications such as neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease.
To manage hyperglycemia effectively:
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regular check-ups and home monitoring can help keep blood sugar within target ranges.
- Healthy Eating: Opt for a balanced diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats while moderating sugar intake.
- Stay Active: Incorporate physical activity into your routine, as exercise helps the body use insulin more effectively.
- Consult Healthcare Professionals: Regular consultations with doctors or diabetes educators can help tailor management plans that suit individual needs.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of hyperglycemia is the first step towards effective management and prevention of serious health issues. Staying informed about one’s condition, implementing healthy lifestyle choices, and maintaining regular medical oversight can help individuals lead healthier, more vibrant lives. If you suspect that you or someone you know may be experiencing hyperglycemia, it is vital to seek medical advice promptly. By taking proactive steps, you can better manage your health and minimize the risks associated with high blood sugar levels.

Grant Edward Rayner