Unlocking the Nutritional Powerhouse: The Mighty Beet
Overview of what beets are and their historical significance
Beets are root vegetables that have been cultivated for thousands of years. They are known for their vibrant red color and sweet earthy flavor. Beets have a long history of being used for both culinary and medicinal purposes. They were originally grown for their leaves which are also edible and have a similar taste to spinach.
The ancient Romans used beets as a natural remedy for fevers and constipation. Today, beets are popular in a variety of cuisines and are valued for their nutritional benefits including high levels of vitamins and antioxidants. So what are the health benefits of eating beets?
Nutritional profile: key vitamins and minerals found in beets

Beets are a highly nutritious vegetable that is packed with essential vitamins and minerals. One of the key vitamins found in beets is vitamin C, which is important for immune function, skin health, and collagen production.
Beets also contain vitamin B6 which plays a crucial role in brain development and function as well as in the production of neurotransmitters. In addition, beets are a good source of folate which is essential for cell division and DNA synthesis.
When it comes to minerals, beets are rich in potassium, which is important for maintaining healthy blood pressure and proper muscle function. They also contain manganese, which is necessary for bone health, metabolism and antioxidant function.
Furthermore, beets are a good source of iron which is essential for the production of red blood cells and oxygen transport in the body. Overall, beets are a powerhouse of essential vitamins and minerals that are vital for overall health and well-being.
Highlighting the unique compounds in beets, like betalains
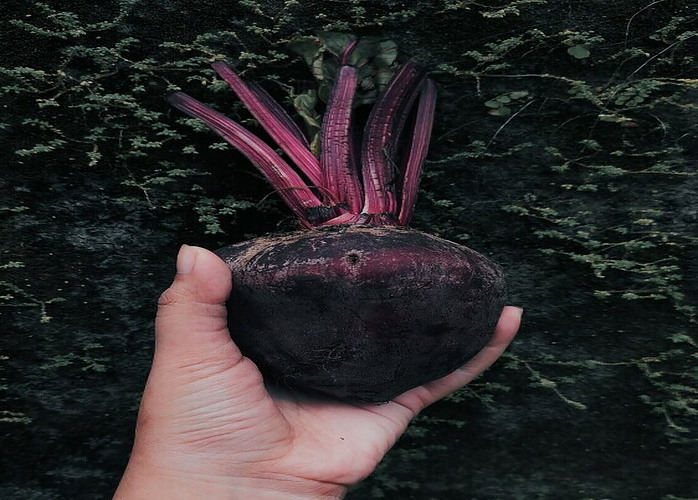

Beets are a unique vegetable that contains a variety of compounds, including betalains which are responsible for the vibrant red and yellow colors found in beets. Betalains are a class of antioxidants that have been studied for their potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and detoxification properties. These compounds are not commonly found in other vegetables making beets a standout choice for those looking to incorporate a diverse range of nutrients into their diet.
Additionally, betalains are known for their potential role in supporting cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Overall, beets are a great source of unique compounds like betalains that can contribute to a well-rounded and nutritious diet.
How the nutritional elements in beets can contribute to overall health
Beets are a highly nutritious vegetable that can contribute to overall health in various ways. They are a good source of essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, potassium, and folate. These nutrients can help support a healthy immune system, regulate blood pressure and promote healthy cell function.
Beets are also high in dietary fiber which can aid in digestion and help maintain a healthy weight. Additionally, beets contain nitrates which have been shown to improve blood flow and enhance athletic performance. Consuming beets as part of a balanced diet can provide numerous health benefits and contribute to overall well-being.

The Heart of the Matter: Beets and Cardiovascular Well-being
Exploring beets’ ability to lower blood pressure
Beets have gained attention for their potential to lower blood pressure due to their high nitrate content. Nitrates are converted into nitric oxide in the body, which helps to relax and dilate blood vessels, leading to improved blood flow and lower blood pressure.
Several studies have shown that consuming beet juice or beet supplements can lead to a significant decrease in blood pressure levels particularly in individuals with hypertension. Additionally, beets are also rich in other nutrients such as potassium which is known to help regulate blood pressure.
While more research is needed to fully understand the effects of beets on blood pressure, incorporating them into a balanced diet may be a beneficial strategy for managing hypertension.
The role of nitrates in beets and their impact on heart health
Nitrates are naturally occurring compounds found in various vegetables, including beets. When consumed, nitrates are converted into nitric oxide in the body, which plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and improving overall cardiovascular health.
Studies have shown that the consumption of nitrates from beets can lead to a decrease in blood pressure as well as improved blood flow and oxygen delivery to the heart and other organs. This can ultimately reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. Additionally, the nitric oxide produced from nitrates in beets can help to relax and dilate blood vessels leading to improved circulation and lower risk of blood clots.
As a result, incorporating beets into a balanced diet can have a positive impact on heart health. It is important to note that while nitrates in beets are beneficial for heart health, excessive consumption of nitrates from processed foods and cured meats has been linked to potential health risks. Therefore, it is essential to consume nitrates from natural sources, such as beets, in moderation as part of a healthy diet.
How eating beets may help reduce the risk of heart disease
Beets contain high levels of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds which can help to reduce the risk of heart disease by protecting against oxidative stress and inflammation. Some studies have also suggested that regular consumption of beets may help to improve cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of plaque buildup in the arteries. Including beets in a balanced and varied diet may be a simple and effective way to support heart health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Discussion of research studies supporting beets’ benefits for the cardiovascular system
Several research studies have provided evidence supporting the benefits of beets for the cardiovascular system. A study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology found that drinking beet juice significantly increased nitric oxide levels and improved exercise performance in healthy adults.
Another study published in the American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology showed that dietary nitrate supplementation from beets improved endothelial function and reduced blood pressure in individuals with hypertension.
Furthermore, a meta-analysis published in the Journal of Human Hypertension concluded that beetroot juice supplementation significantly lowered blood pressure in both healthy individuals and those with hypertension.
These findings suggest that incorporating beets into the diet may have beneficial effects on cardiovascular health. However, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind these effects and to determine the optimal dosage and duration of beet supplementation for cardiovascular benefits. Nonetheless, the existing evidence indicates that beets may be a valuable contributor to heart and cardiovascular system health.
From Root to Leaf: The Health Benefits of Beet Greens
Introduction to beet greens, the often-overlooked leafy tops

Beet greens, the leafy tops of the beetroot plant, are often overlooked in favor of the root itself. However, these greens are not only delicious but also highly nutritious. They are packed with vitamins A, C, and K, as well as minerals like iron, calcium and potassium. Beet greens taste like spinach, one of my favorite vegetables. My wife and I regularly take the beet tops which will regenerate. Accordingly, you can take the tops two or even three times during the summer!
Beet greens can be eaten raw in salads, sautéed as a side dish, or added to soups and stews for an extra boost of flavor and nutrients. They have a slightly bitter taste, similar to other leafy greens like kale or Swiss chard, but can be balanced with the right seasonings and cooking methods. Next time you buy beets, don’t throw away the greens! Give them a try and discover their delicious and healthful benefits!
Nutritional breakdown of beet greens and their health advantages
In terms of nutritional breakdown, beet greens are an excellent source of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as minerals such as potassium, magnesium, and iron. They also contain high levels of fiber which can aid in digestion and promote a feeling of fullness.
Additionally, beet greens are rich in antioxidants which can help protect the body from oxidative stress and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Consuming beet greens can also contribute to healthy bones as they contain high levels of vitamin K and calcium. Furthermore, the nitrates found in beet greens have been linked to improved cardiovascular health as they can help lower blood pressure and improve blood flow. Overall, including beet greens in your diet can provide a wide range of health benefits and contribute to overall well-being.
Linking beet greens to improved bone health and vision
Beet greens, the leafy green tops of beets, have been linked to improved bone health and vision due to their high nutrient content. These greens are rich in vitamin K, which plays a crucial role in bone health by helping to regulate calcium levels and promote bone mineralization.
Additionally, beet greens are a good source of vitamin A which is essential for maintaining healthy vision. Vitamin A is known for its role in promoting good eyesight and reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration. Furthermore, beet greens also contain other important nutrients such as calcium, iron and antioxidants, all of which contribute to overall health and well-being.
Including beet greens in your diet can be a simple and effective way to support your bone health and vision. Whether added to salads, smoothies or sautéed as a side dish, beet greens are a versatile and nutritious addition to any meal.
Simple ways to incorporate beet greens into daily meals
One easy way to use beet greens is to sauté them with garlic and olive oil as a side dish. You can also add them to salads for an extra boost of nutrients. Another option is to blend beet greens into a smoothie for a refreshing and healthy drink.
If you enjoy cooking with grains, consider adding chopped beet greens to your quinoa or rice dishes for added flavor and nutrition. Additionally, you can use beet greens as a topping for homemade pizzas or mix them into pasta dishes for a pop of color and nutrients. With so many ways to incorporate beet greens into your meals, it’s easy to make them a regular part of your daily diet.

Beets in Practice: Incorporating Beets Into A Healthy Lifestyle
Creative and tasty ways to add beets to your diet
There are numerous creative and tasty ways to incorporate beets into your meals, whether you enjoy them raw, roasted, or pickled. One popular way to enjoy beets is by adding them to salads. Their natural sweetness and vibrant color can add a unique twist to your favorite salad recipe.
Another way to incorporate beets into your diet is by blending them into a smoothie. Beets can add a subtle sweetness and earthy flavor to your smoothie, while also providing a boost of essential nutrients. Additionally, you can try incorporating beets into your baked goods, such as beet brownies or beet cake, for a unique and delicious treat.
You can also experiment with adding beets to your favorite soups or stews for a hearty and nutritious addition. Whether you are a fan of savory or sweet dishes, there are countless ways to enjoy the versatile and nutritious beet in your daily meals. See our special recipe for Superhero Sauteed Tops at the bottom of this post!
The importance of considering dietary balance and moderation

When it comes to maintaining a healthy diet, it is essential to consider dietary balance and moderation. Beets are a nutritious vegetable that can be included in a balanced diet as they are low in calories and high in essential nutrients such as fiber, folate, and vitamin C.
However, it is important to consume beets in moderation as they are also high in natural sugars. Consuming too many beets can lead to an excessive intake of sugar which can have negative effects on blood sugar levels and overall health.
Therefore, it is important to incorporate beets into a well-rounded diet in appropriate portions along with a variety of other fruits, vegetables, proteins and whole grains. By considering dietary balance and moderation, individuals can ensure that they are getting the necessary nutrients while also maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Potential side effects to be mindful of when consuming beets
When consuming beets, it is important to be mindful of potential side effects that may arise. While beets are a nutritious and delicious vegetable, they can also cause some adverse reactions in certain individuals.
One potential side effect of consuming beets is beeturia, which is the passing of red or pink urine after eating beets. This is a harmless condition that occurs in some people due to the presence of betalain pigments in beets.
Additionally, beets are high in oxalates, which can contribute to the formation of kidney stones in individuals who are prone to this condition. It is important for those with a history of kidney stones to consume beets in moderation and to stay well-hydrated to reduce the risk of stone formation.
Furthermore, some individuals may experience digestive discomfort such as bloating, gas or diarrhea after consuming beets, particularly if they have a sensitivity to FODMAPs, which are fermentable carbohydrates found in certain foods.
It is advisable for those with digestive issues to monitor their intake of beets and to consult with a healthcare professional if they experience persistent discomfort. Overall, while beets offer numerous health benefits, it is important to be aware of these potential side effects and to consume them in moderation, especially for those with specific health concerns.

Building a narrative that connects beets with a holistic approach to health
Beets have long been associated with a variety of health benefits and building a narrative that connects them with a holistic approach to health can be incredibly powerful. Beets are packed with essential nutrients, including fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them an excellent addition to a balanced diet.
They are also rich in antioxidants, which can help reduce inflammation and protect against chronic diseases. Additionally, beets have been shown to support heart health, improve athletic performance and even enhance brain function.
When we consider the holistic approach to health, it’s important to recognize that our physical health is closely tied to our mental and emotional well-being. Beets can contribute to overall wellness by providing nutrients that support both physical and mental health.
Furthermore, the vibrant color of beets is a visual reminder of the importance of incorporating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into our diets! Doing so can help promote overall health and wellness. By building a narrative that connects beets with a holistic approach to health, we can emphasize the importance of nourishing our bodies with nutrient-dense foods that support our overall well-being.
I hope you have enjoyed this content! But I’d like to hear from you as well. Do you have ways to incorporate beets into your diet not mentioned here? If so, please let us know in the comments section below. Also, if you have questions please ask! Finally, if you’d like to be notified as updates are made please enter your name and best email in the form below!

Grant Rayner
Superhero Sauteed Beet Tops
INGREDIENTS
- 1 bunch beets (about 4 beets) with lush green tops attached
- 1 tbsp olive oil
- 2 large garlic cloves, thinly sliced or minced
- 1 tsp fresh lemon juice
- kosher or fine sea salt
- freshly ground pepper
Optional Seasonings and Ingredients
- Cayenne, red pepper flakes, smoked paprika, cumin, ginger, basil, oregano, coriander, raw cacao, and curry pair well with beet greens.
- Red wine vinegar or apple cider vinegar compliment the flavor of beet greens as do gourmet olive oils, such as truffle olive oil and rosemary olive oil. Toasted sesame oil with beet greens is another delicious combination.
Beet It !
The flavor of beet greens is comparable to chard and spinach, so flash boiling, steaming, or sauteing the greens reduces the seemingly bitter taste.
DIRECTIONS
1. Trim off the greens, leaving 1 inch of the stem attached to each root. Reserve the roots for beet recipes.
2. Trim and discard the thick, fibrous stems from the greens and remove any wilted or spotted leaves. See tips for selecting quality beets and beet greens.
3. Stack the leaves, and then cut the stack in half lengthwise through the center vein.
4. Chop the greens crosswise into large pieces, about 2 inches wide.
5. Rinse the greens in several changes of cold water until they are clean and the water is clear.
6. Dry them in a salad spinner or blot dry with paper towels.
7. In a large sauté pan, heat the oil over medium heat and swirl to coat the pan bottom.
8. Add garlic and sauté until soft but not brown, about 1 minute.
9. Add the greens and toss with tongs until wilted but still crisp-tender and bright green, about 3 minutes.
10. Add the lemon juice. Season greens lightly with salt and pepper, and then give the greens a final toss in the pan.
Serve immediately.
Resources
Bradford, Alina. (2015). Vitamin K: Sources & Benefits. Life Science Publication. Retrieved from https://www.livescience.com/51908-vitamin-k.html.
Cornish, Stacey. et al. (2008). The Role of Vitamins and Minerals in Psychiatry. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3046018/.
Iron and Your Health. (2015). Harvard Health Publishing. Harvard Medical School. Retrieved from https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/iron-and-your-health.
Nutrition Data. (2014). Retrieved from https://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/vegetables-and-vegetable-products/2353/2.
Robinson, Jo. (2013). Eating on the Wild Side. New York: Little, Brown and Company.
Splittstoesser, W. E. (2014). Beet. In Public Libraries. Retrieved from http://www.worldbookonline.com/pl/infofinder/article?id=ar052980.
Stanaway, Luke. et al. (2017). Performance and Health Benefits of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5707643/.
