Understanding Radiculopathy: A Medical Perspective
Radiculopathy is a medical condition characterized by pain, weakness, numbness or tingling that radiates along the path of a nerve. This condition occurs when a spinal nerve root is compressed, irritated or inflamed. It is commonly caused by a herniated disc spinal stenosis, or degenerative disc disease.
Radiculopathy can affect any nerve in the body, but it most commonly occurs in the neck (cervical radiculopathy) or lower back (lumbar radiculopathy). Treatment may include physical therapy, medication, injections, or in severe cases, surgery. Proper and accurate diagnosis and early intervention are crucial in managing radiculopathy and preventing long-term complications.
Diagnostic techniques used to identify radiculopathy
Radiculopathy is a condition characterized by nerve root compression resulting in symptoms such as pain, weakness, and numbness in the affected area. In order to accurately diagnose radiculopathy, various diagnostic techniques are employed by healthcare professionals. These techniques typically include a thorough physical examination to assess reflexes, muscle strength and range of motion.
Imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI scans and CT scans may also be utilized to visualize the affected nerves and surrounding structures. Furthermore, electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies can be employed to evaluate nerve function and pinpoint the location of nerve damage. By utilizing a combination of these diagnostic techniques, healthcare providers are able to accurately identify the nature and extent of the condition in order to develop an appropriate treatment plan, leading to improved patient outcomes.
The symptoms of radiculopathy can vary widely, depending on the severity and location of the nerve impingement. Proper diagnosis of radiculopathy is crucial in order to determine the extent of the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan. This typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans.
It is important for healthcare providers to accurately pinpoint the affected nerve root(s) in order to effectively manage the symptoms and prevent further complications. A misdiagnosis or delay in treatment can lead to prolonged pain and disability for the patient. It is therefore imperative that healthcare professionals have a high level of suspicion when a radiculopathy has been diagnosed and utilize appropriate diagnostic tools to ensure the diagnosis is accurate and that intervention is timely.
Causes
There are several potential causes of radiculopathy, including herniated discs, degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, and foraminal stenosis. A herniated disc occurs when the gel-like center of a spinal disc ruptures through a weakened or torn outer wall and presses on a nerve root.
Degenerative disc disease is a condition in which the discs in the spine break down over time, causing bone spurs and nerve compression. Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal that puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. Foraminal stenosis is a narrowing of the passageways through which nerves exit the spinal column, leading to nerve compression.
Other less common causes of radiculopathy include trauma, tumors, infections and inflammatory conditions. In order to properly diagnose and treat radiculopathy, a thorough evaluation by a medical professional is essential. Treatment options may include physical therapy, medications, injections and, in severe cases, surgery.
Living with Radiculopathy: Challenges and Adaptations
Nature and extent of radiculopathy and its impact on daily activities
Radiculopathy, a condition characterized by the compression or irritation of spinal nerve roots can, depending on the severity of the condition, have a significant impact on an individual’s daily activities. Common symptoms include pain, weakness and numbness in the affected areas, which can be debilitating and severely limit one’s ability to perform routine tasks. The nature and extent of the radiculopathy can vary greatly depending on the severity of the nerve compression and the specific location of the affected nerve root.
In some cases, individuals may experience mild discomfort or tingling sensations, while others may suffer from excruciating pain and muscle weakness. Regardless of the severity, radiculopathy can interfere with a person’s ability to work, exercise or engage in activities they once enjoyed. Seeking timely medical attention and appropriate treatment is essential in managing the symptoms and improving one’s quality of life.
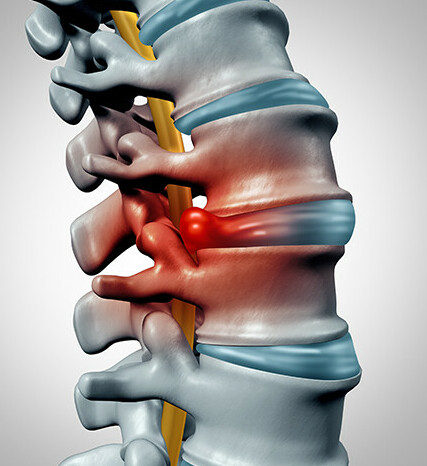
Physical limitations and functional impairments due to radiculopathy
Radiculopathy refers to a condition in which a nerve root in the spine is compressed, causing pain, weakness, or numbness in the area of the body that the nerve supplies. This condition can result in physical limitations and functional impairments that significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
The pain and discomfort associated with radiculopathy can restrict movement and make it difficult to perform everyday tasks such as walking, bending or lifting objects. The weakness and numbness that often accompany a radiculopathy can lead to difficulties with coordination, balance and fine motor skills. These physical limitations can make it challenging to participate in activities that were once enjoyable or essential for daily living, such as exercising, working or even completing simple household chores.
Moreover, the chronic nature of radiculopathy can result in long-term disability and dependency on others for assistance with basic self-care activities. A diagnosis of radiculopathy can have a profound impact on an individual’s overall well-being, creating barriers to independence and diminishing their overall functional abilities.
Strategies for managing symptoms and improving quality of life
There are various strategies available to manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. Physical therapy, which focuses on strengthening and stretching exercises, can help alleviate pain and improve mobility. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants can also provide relief from discomfort.
In more severe cases, steroid injections or surgical interventions may be necessary. It is important for individuals with radiculopathy to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to their specific needs. By addressing symptoms proactively and engaging in appropriate therapies, individuals with radiculopathy can experience improvements in their quality of life.
The role of rehabilitation and assistive devices in adapting to limitations
Radiculopathy, a condition caused by compression or irritation of the spinal nerves, can result in significant limitations in mobility and function for those affected. In these cases, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in helping individuals adapt to their new physical limitations and regain independence.
Physical therapy programs can help improve strength, flexibility, and coordination, allowing patients to better manage their symptoms and prevent further deterioration. In addition, assistive devices such as braces, walkers or ergonomic tools can provide support and assistance in performing daily activities.
By combining rehabilitation techniques and the use of assistive devices, individuals with radiculopathy can enhance their quality of life and maintain a level of functionality despite the challenges posed by their condition.

Grant Rayner B.Comm., LL.B.
Langdon Law